
Respiratory system Artofit
The act of breathing in oxygen. Exhaling. The act of breathing out carbon dioxide. Respiratory system The respiratory system is made up of the organs included in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The respiratory system is divided into two areas: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract.

Respiratory Tract, Drawing, Anatomical Airway, Nasal Pharynx, Showing... News Photo Getty Images
NIH HHS USA.gov The airway, or respiratory tract, describes the organs of the respiratory tract that allow airflow during ventilation. [1] [2] [3]They reach from the nares and buccal opening to the blind end of the alveolar sacs. They are subdivided into different regions with various organs and tissues to perform specific functions.
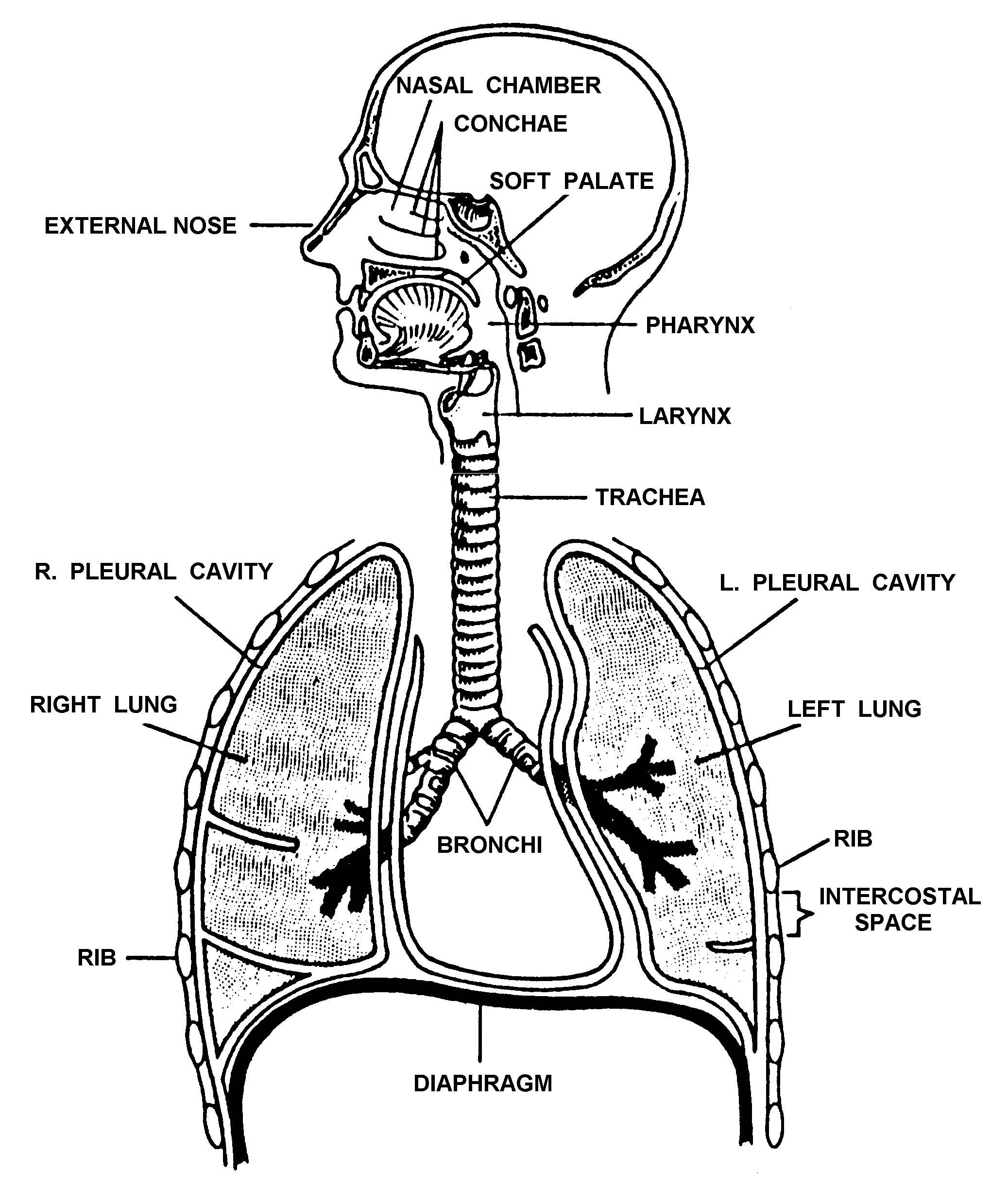
15. THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Figure 22.3.1 - Boyle's Law: In a gas, pressure increases as volume decreases. Pulmonary ventilation is dependent on three types of pressure: atmospheric, intra-alveolar, and interpleural. Atmospheric pressure is the amount of force that is exerted by gases in the air surrounding any given surface, such as the body.

Las Nike Air Max 95 “Anatomy of Air” son las zapatillas para llevar con todo (y sin nada más
This article will discuss the anatomy and function of the respiratory system. Contents Upper respiratory tract Nasal cavity Paranasal sinuses Pharynx Larynx Lower respiratory tract Tracheobronchial tree Lungs Microanatomy Function Clinical aspects Upper respiratory tract infections Lower respiratory tract infections Sources + Show all

Respiratory Anatomy Ordered Flow of Air YouTube
There are 3 major parts of the respiratory system: the airway, the lungs, and the muscles of respiration. The airway, which includes the nose, mouth, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles, carries air between the lungs and the body's exterior. The lungsmycontentbreak act as the functional units of the respiratory system by.

Airway Management Oxygenation and Ventilation Thoracic Key
Respiration begins at the nose or mouth, where oxygenated air is brought in before moving down the pharynx, larynx, and the trachea.The trachea branches into two bronchi, each leading into a lung.Each bronchus divides into smaller bronchi, and again into even smaller tubes called bronchioles.At the end of the bronchioles are air sacs called alveoli, and this is where gas exchange occurs.

Lower Respiratory Notes Dr. Jeannine Durdik
The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages called the respiratory tract, through which air flows into and out of the body. The respiratory tract has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. The organs in each division are shown in Figure 16.2.2 16.2.

Lower Respiratory System
The anatomy of the upper airway can be broken down into the nose, mouth, and throat. The medical terms for these are the nasopharynx and oropharynx/larynx. NOSE (Nasopharynx): The nose is the primary airway used by most conscious adults to breathe.
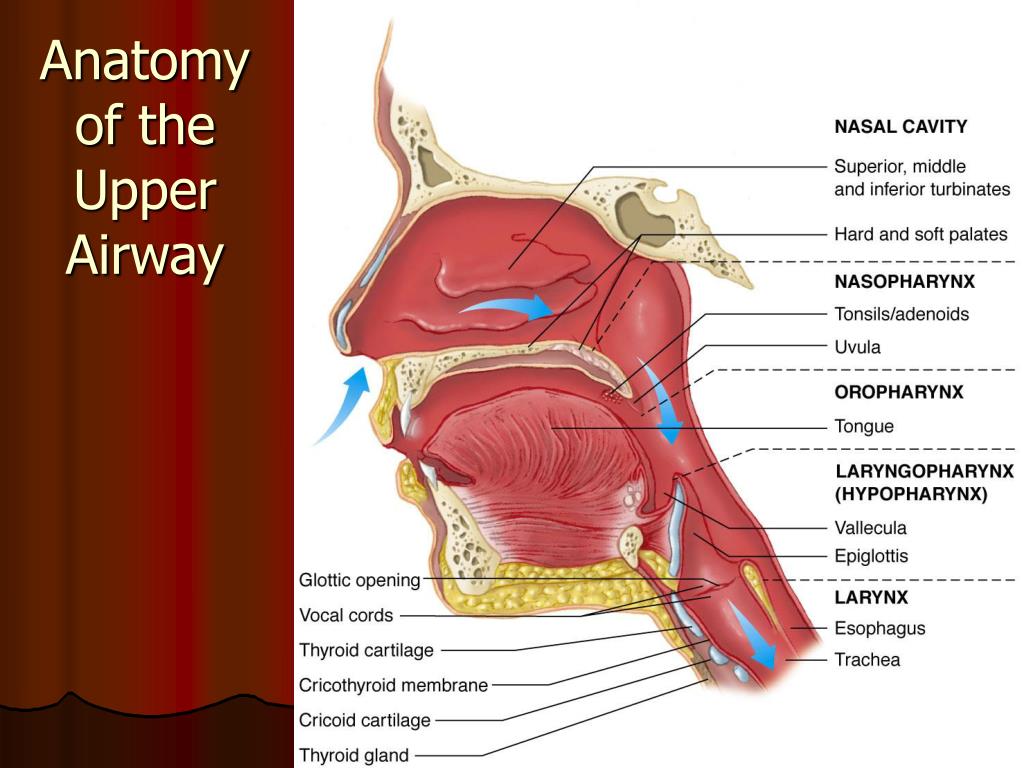
PPT Airway Management Part 1 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1341784
The respiratory system aids in breathing, also called pulmonary ventilation. In pulmonary ventilation, air is inhaled through the nasal and oral cavities (the nose and mouth). It moves through the pharynx, larynx, and trachea into the lungs. Then air is exhaled, flowing back through the same pathway. Changes to the volume and air pressure in.

Human Respiratory System Diagram Class 10 CBSE Class Notes Online Classnotes123
The primary function of the respiratory system is gas exchange between the external environment and an organism's circulatory system. In humans and other mammals, this exchange balances oxygenation of the blood with the removal of carbon dioxide and other metabolic wastes from the circulation. Bronchial anatomy: The pulmonary alveoli are the.

The Process of Breathing · Anatomy and Physiology
In this chapter, we scope the importance of functional anatomy and physiology of the upper airway. The upper airway has an important role in transporting air to the lungs. Both the anatomical structure of the airways and the functional properties of the mucosa, cartilages, and neural and lymphatic tissues influence the characteristics of the air that is inhaled. The airway changes in size.

Release Date Nike Air Max 95 Anatomy of Air
The nasal bone is one of a pair of bones that lies under the root and bridge of the nose. The nasal bone articulates superiorly with the frontal bone and laterally with the maxillary bones. Septal cartilage is flexible hyaline cartilage connected to the nasal bone, forming the dorsum nasi.

The Anatomy Of Air The Artists Behind The Xray Nike News
Nike Air Max 95 Anatomy of Air GID Dernière vente : -- Aucune vente pour l'instant Voir les demandes Voir les offres Voir les ventes Vérifié par StockX État : neuf Notre engagement Produits similaires Nike Air Max 95 Anatomy of Air (Women's) Demande la plus basse €89 Dernière vente : €125 Nike Air Max 95 GID coloris os clair Demande la plus basse
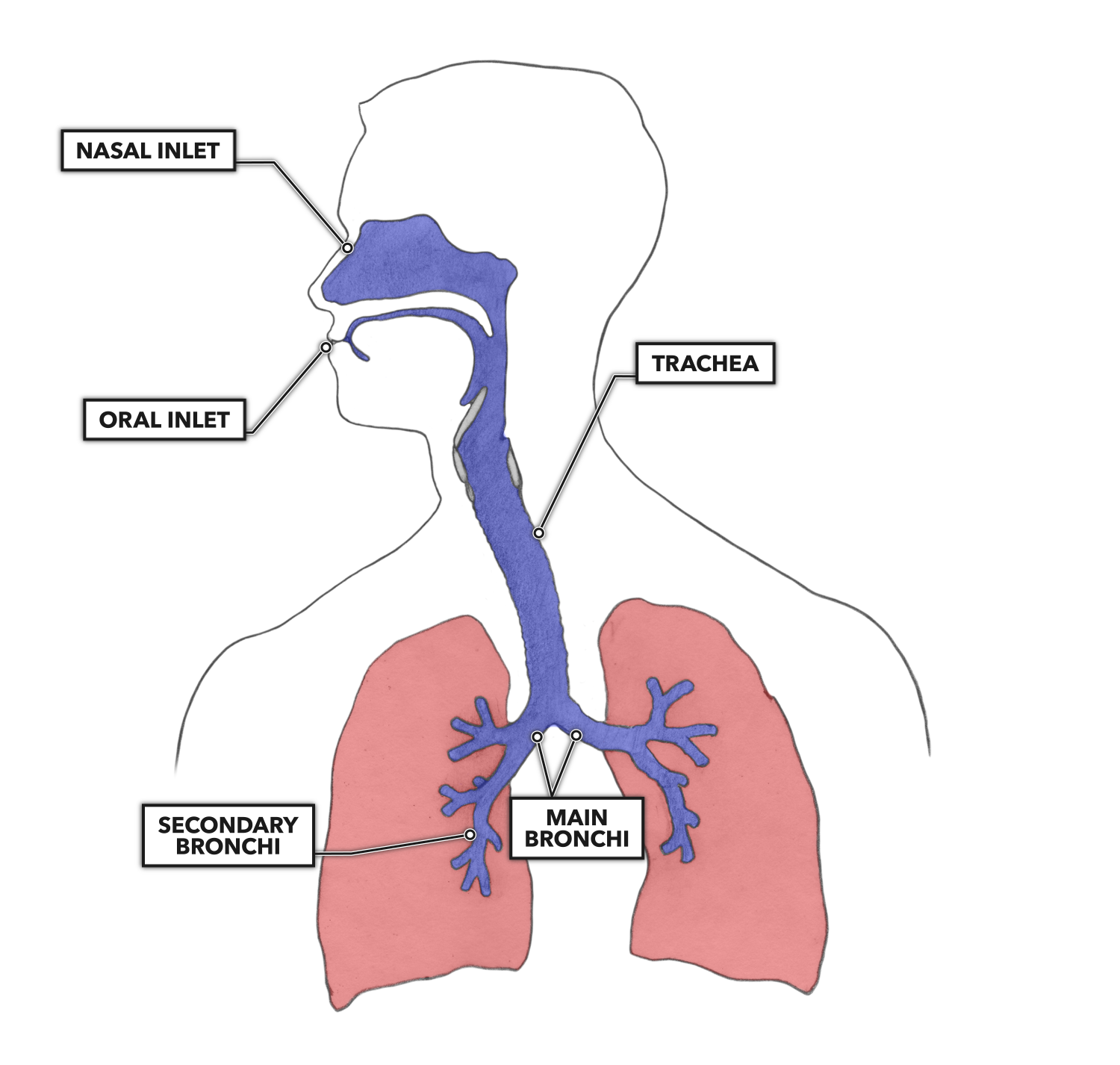
CrossFit Lung Anatomy The Airway and Alveoli
human body maps respiratory system Respiratory The respiratory system includes the organs, tissues, and muscles that help you breathe. It helps distribute oxygen throughout your body while.

22.1 Organs and Structures of the Respiratory System Anatomy & Physiology
Anatomy of breathing: Process and muscles of respiration | Kenhub Anatomy of breathing Author: Adrian Rad BSc (Hons) • Reviewer: Elizabeth O. Johnson, PhD Last reviewed: August 31, 2023 Reading time: 20 minutes Recommended video: Respiratory system [23:23] Main structures of the respiratory system. Horizontal fissure of right lung
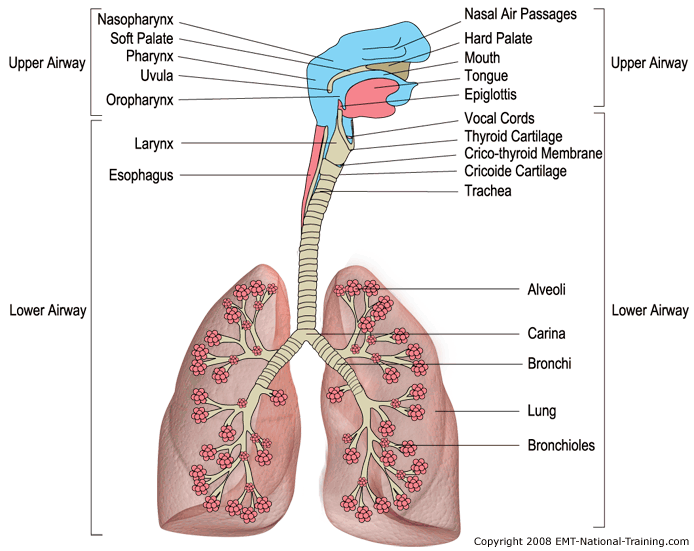
Lower Airway Anatomy
Air Max 95 Remember the revolution. 1987 saw the birth of the Air Max lineage, showcasing visible Air for the first time. What began as an experiment in cushioning soon evolved into an icon on the track and the streets. Over the years, it's been re-imagined and re-tooled, but the heritage always remains.